It might seem surprising that a 12th-century mathematician’s work is still relevant in today’s binary options trading, but Fibonacci’s discoveries play a key role. Traders use Fibonacci to identify support and resistance levels, trade harmonic patterns, and predict retracement depths.

Key Facts About Fibonacci Retracement Strategy:
- Fibonacci is based on thousands of years of mathematical discoveries that apply to forecasting the depth of retracements in traded markets
- Although many Fibonacci tools exist (arcs, time zones, fans, channels, etc.), the retracement tool is the most commonly used
- Traders use Fibonacci retracements to identify potential support and resistance in conjunction with other signals
- Fibonacci extensions are attached to the retracement tool, and help offer profit levels and future support and resistance
- Although Fibonacci is effective, traders shouldn’t use it as a standalone tool
What Is Fibonacci Trading?
Fibonacci refers to different technical tools based on the Fibonacci sequence or Fibonacci series. The theory is traced to Leonardo Fibonacci, a super-Italian mathematician from the Middle Ages. Fibonacci created a manuscript named ‘Liber Abaci’ or The Book of Calculation in 1202.
This is where the math genius introduced the Fibonacci series, a series of numbers where each is the total of the preceding two, ex: 1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21,34, 55, 89, and so on. A certain ‘golden ratio’ or ‘divine proportion’ exists between these figures, where each number is about 1.618 times greater than the last.
For example, dividing 34 into 21 equals 1.619; dividing 89 into 55 equals 1.618; dividing 13 into 8 gives you 1.625, etc.
The golden ratio exists in numerous nature-based occurrences like bee hives, tree branches, DNA molecules, flower petals, hurricanes, and even parts of the human face.
1.618 isn’t the only special number in the Fibonacci sequence. 1.382 is another key figure derived from dividing a number in the series by another two places right of it. For example, five divided by 13 equals roughly 0.384.
Fibonacci tools generally center around the following percentages:
- 0.236 (or 23.6%)
- 0.382 (or 38.2%)
- 0.5 (or 50%)
- 0.618 (or 61.8%)
- 0.786 (or 78.6%)
- 1 (or 100%)
These represent areas of support and resistance for any traded market in binary options. While many Fibonacci tools (like time zones, arcs, fans, and channels) exist, binary options traders primarily use retracements.
Extensions are an addition to the Fibonacci retracements that project future levels. We express these as:
- 1.236 (or 123.6%)
- 1.382 (or 138.2%)
- 1.50 (or 150%)
- 1.616 (or 1.618%), and so on.
How to Use Fibonacci Retracements in Binary Options:

The retracement tool should be available with all charting platforms offered by binary options brokers. It consists of horizontal lines that enlarge or tighten based on the price action range a trader covers on a chart.
Here are the basic rules when plotting the tool:
Traders measure from the tip of the high to the tip of the low for a bearish move.
Traders measure from the tip of the low to the tip of the high for a bullish move.
Traders will wait for the price to retrace at a certain retracement level in both scenarios.
See our strategy tutorial here on Youtube:
Bearish Example on the XAU/USD or Gold Chart & The Inverse
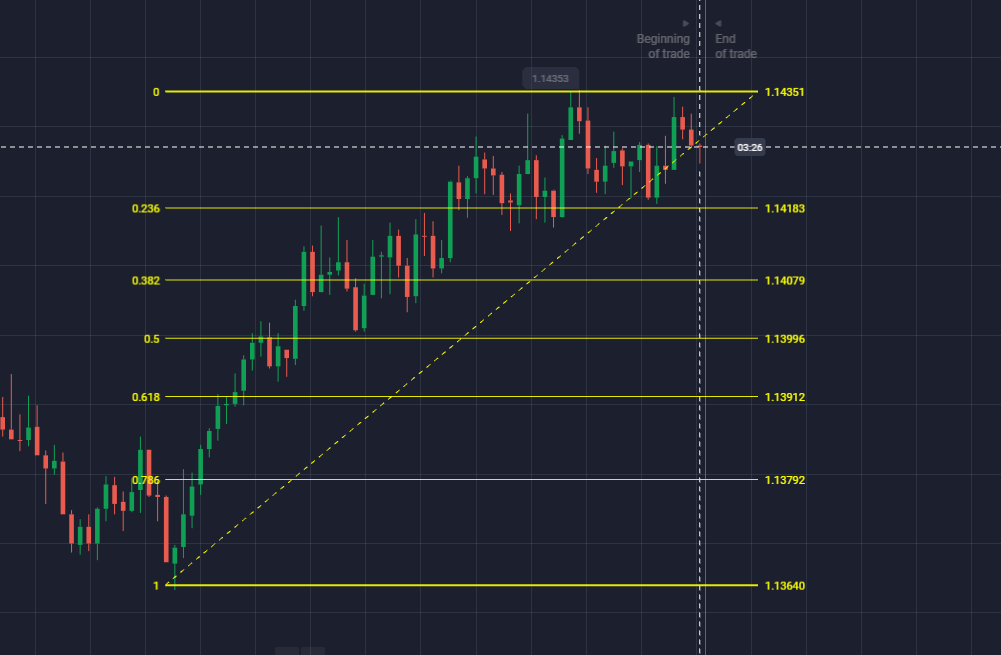
Let’s look at the images below for examples.

The first is a bearish example on the XAU/USD or gold chart, considering the marked high at $2065.530 and low at $1984.305. One would simply plot the retracement tool from $2065.530 and drag it to $1984.305.
The arrow marks the retracement to the different Fib levels where traders can expect resistance.

In the inverse, let’s say EUR/AUD increased from 1.63506 (low) to 1.66119 (high). One would draw the Fib from the low to the high. The arrow marks the retracement to the different Fib levels where traders can anticipate support.
It’s worth noting that Fibonacci shouldn’t be the sole trigger to buy or sell; it simply estimates where a market will likely correct itself. It’s up to the analyst to determine whether a valid signal appears at that point.
The Fibonacci extensions are purely for projecting potential profit levels. You should draw these in the opposite way compared to the retracement tools. The extension levels (123.6%, 138.2%, etc.) should appear at the bottom for a bearish move and at the top for a bullish move.
Still, extensions don’t apply with most binary options like the up/down and in/out. It can be useful for touch/no and ladder binary options where traders must consider prices breaching certain levels before the expiry time.
Many traders are also curious about the best retracement levels to watch out for. A rule of thumb is that the stronger a move or trend is, the likelier it is to find support or resistance on the 23.6% to 38.2% zones during a correction.
As expected, traders use several tools to determine the strength of such moves. However, any strategy should consider the 50% to 61.8% levels (more so that the 61.8% is considered the ‘golden ratio’) to account for prolonged retracements even during stronger trends.
Markets that exceed the 61.8% zones and reach the 78.6% lines may appear like reversals. Yet, traders can also exploit these moments under certain conditions.
3 Best Strategies for Fibonacci Trading in Binary Options
Most trading strategies using Fib take advantage of pullbacks or corrections in powerful trends. Range-bound or sideways markets should be avoided with Fib.
As expected, binary options traders should combine this tool with other techniques and indicators for better results.
The key is to observe a market once it begins to retrace. Let’s look at the different tactics you can use based on the depth of the retracements.
1. Shallow Retracement Strategies
A shallow pullback happens in rare instances, meaning traders must be extra cautious. A market should be moving in a fast, breakout-like manner. The corrections are smaller than normal, with the asset in question spending little time during this phase.
Binary options traders can use these techniques as reference points:
- Momentum indicators like the Relative Strength Index/RSI should reveal ‘overbought’ or ‘oversold’ (or be close to these areas).
- A fast-moving trend usually respects a trend line of no less than 30° in angle. The greater the angle inclination and the more price touch points on the line, the more powerful that trend is.
- Moving averages play a similar role to the trend line. The greater periods (i.e., 50 days, 100 days, etc.) on higher time frames, along with the trend’s slope, provide clues about trend strength.
Once traders plot their two points, it’s time to wait for the market to reach 23.6%. Speculators should watch out for several trend continuation patterns like triangles, flags, pennants, and wedges for extra confirmation.
Price action formation can also be effective. For instance, a clearly defined pin bar or other candle with a small body and a long tail or wick signals a correction is likely over. Finally, traders can align the 23.6-38.2% zones with pre-marked key levels in a higher time frame.
After getting enough confirmation, traders can enter the trade with a buy/call or sell/put option after the market has hit the 23.6% or 38.2% point on the Fib retracement lines.

2. Medium Retracement Strategies
These strategies apply when the market retraces between 50-61.8%. These are normal trends that don’t move unusually fast while demonstrating a clear directional bias. Moreover, the depth of the corrections is higher, with the asset being traded spending more time compared to the shallow trends.
Binary options traders can use these techniques as reference points:
- Momentum indicators like the RSI should reflect below or above 50, a reasonable midpoint. While not overly bullish or bearish, it suggests that the market leans more to one side than the other.
- The average trend usually has an inclination of 30° or less when studying its trend line.
After plotting the necessary points, traders anticipate the price dropping or rising between 50-61.8% of the Fib. As with the last example, one can use continuation patterns like triangles, flags, pennants, and wedges. Likewise, the same price action formations may prove effective.
Traders can execute a buy/call or sell/put trade after receiving sufficient confirmation and when the price has clearly reached the desired levels.
3. Deeper pullback strategies
Deep retracements between the 61.8-78.6% areas may suggest that the trend has turned into a reversal. Yet, markets do continue to resume in their predominant direction, and this is something binary options traders can exploit.
In the previous scenarios, traders had to observe the current trend’s strength. Here, it’s more about determining whether a retracement will be deep. This process is quite tricky. The best way is to observe the retracement leg using a momentum indicator like the RSI. Instances of price entering the overbought/oversold zones from the 50% levels indicate the likelihood of it reaching 61.8% or further.
As with the other examples, traders can look for continuation and price action patterns for further confirmation once the market is between 61.8-78.6% before entering using a buy/call or sell/put position.
What Are Pros And Cons of Fibonacci Trading With Binary Options?

- Objectivity: Provides clear retracement levels, enabling precise decision-making
- Simplicity: Once learned, plotting Fibonacci becomes straightforward and intuitive
- Compatibility: Works well with other analysis tools without cluttering charts
- Versatility: Useful across various markets and trading strategies
- Predictive Power: Helps traders anticipate support and resistance zones based on mathematical ratios
- Subjective Interpretation: Despite its objectivity, it’s difficult to predict exact market corrections
- Self-Fulfilling Bias: Fibonacci levels often reflect collective trader behavior rather than market fundamentals
- Over-Reliance: Relying solely on Fibonacci can lead to missed signals without the support of other tools
What are Alternative Indicators for The Fibonacci Tool?
Moving averages are the best alternative to Fibonacci. They can act as ‘dynamic’ support and resistance. Like a trend line, traders can look for retracement swings on the moving averages where the price will stall before continuing in its predominant direction.
Other alternatives that incorporate moving averages include:
- Bollinger Bands – this tool consists of three moving averages as a bands for determining overbought and oversold conditions.
- Ichimoku cloud – this indicator uses moving average-like lines to create a ‘cloud’ to forecast support and resistance. It’s also used to observe momentum and trend direction.
Fibonacci stands out for its mathematical precision, but it works best when paired with other indicators as a supplement. Tools like moving averages and Ichimoku clouds help forecast support and resistance by plotting price trends on a chart.
Conclusion
Traders can quickly master Fibonacci once they grasp its core concepts, with retracements and extensions being the most commonly used variations. However, it’s important not to rely solely on Fibonacci; combining it with other tools like moving averages, RSI, price action, and trend lines is key for more accurate analysis.
Most Asked Questions:
Which are the best Fibonacci retracement levels to trade?
Retracements can happen at any Fib level, depending on the market conditions. Binary options traders must develop different strategies to cover all the potential areas where the price may retrace.
How do you calculate Fibonacci retracement levels?
The Fibonacci retracement tool automatically produces the levels as the traders expand or contract the tool across price points.
How accurate is Fibonacci in binary options?
Fibonacci is fairly accurate. Yet, the key is to combine it with other technical tools to have the best trading signals.
How does Fibonacci trading differ from other technical analysis tools?
Fibonacci trading is unique because it relies on precise mathematical ratios derived from the Fibonacci sequence to identify potential support and resistance levels in the market. While other tools like moving averages or trend lines focus on broader patterns, Fibonacci’s accuracy allows traders to predict more specific retracement points, making it a valuable supplement to other technical indicators.








